I swear this is the last postapocalypic robot animals post I make in OMM, but I had to dedicate an entry to Metalzoic, an absurd and highly entertaining story told by Pat Mills and Kevin O’Neill, and published by DC Comics and 2000 AD. If tales of amoral robotic gorillas beating up tank-elephants are your bag, you can buy this stirring saga in stores, including here and here.
I will try not to give away too much plot, focusing only on the creatures, but if you were planning on reading this someday, spoilers are inevitable.

Metalzoic is set on Earth during the, well, Metalzoic period. The above timeline explains it far better than I ever could, but suffice to say the Earth belongs to metallic, naturally evolving robot and plants that evolved themselves from prior machinery. There are still pockets of humanity eking out a Mad Max-esque life, but it’s the robots that run this show.

While the story focuses on Armageddon, Amok, and their respective tribes, it is arguably the Traffids that are the true dominant species. These are the mechanical equivalent of plants. Some grow to huge sizes and form dense forests through which other robots seek their food.
One interesting thing about Metalzoic is that it appears that all the robots are sapient and have names. Even the traffids. The specimen above, the equivalent of a pitcher plant, has successfully replicated a human building, down to the details of the interior, and uses this appearance to trick humans into coming in and dissolving in acid. Our heroes realize something is off when the pages of the books inside are blank.

The hero of the story is Armageddon, a robot gorilla and leader of the Mekaka*, a tribe of assorted robot primates. Armageddon, as the header image makes clear, operated on his own brain to remove such trivialities as emotion and compassion, making him ruthless, amoral, and highly respected by the other Mekaka. He even manages to pick up a squishy human and keep her alive somehow.
Armageddon’s special power, and a main plot point and deus ex machina, is to call on the power of Inti, the robot god, and start PUMPING IRON. It is as awesome as it sounds.

Opposing Armageddon is Amok the god-beast, the patriarch of a herd of wheeldebeasts – robo-elephants, the mightiest creatures of the Metalzoic. He’s pictured above with his calf, the little Buboc, next to him. The caterpillar treads and scoop mouth (just above them) strongly suggests ancestry in digging equipment.
Throughout the story Amok leads his herd of wheeldebeasts through various landscapes for a strange, unknown purpose. He is opposed in this by Attila, a younger male seeking to usurp him as leader of the wheeldebeast herd.

Amok is to the left here, Attila to the right. Why are they destroying the Mekaka village? Is this part of Amok’s mysterious goal? Read the book to find out!

Mekaka and wheeldebeasts are far from the only creatures shown, and a good deal of attention is granted to various predators that attack our heroes. Skimiteks are the lions of the Metalzoic, with saber teeth and chainsaw tongues, and they get around on skis, flying through the metal jungle at high speeds.

In this idyllic Metalzoic scene, a skimitek pride (bottom) is at an oilhole, with a girane and her calf (left) and other assorted creatures of the open land.

Polarisaurs are found underneath the frozen poles. Clearly the descendants of submarines, they use periscopes to sight prey on the ice before launching a torpedo at them. They then smash through the ice, grab their victim in their jagged teeth, and sink back into the depths. One of those claims the life of a wheeldebeast before Amok could intercede.

The mirrodillo above has an interesting hunting strategy. It works symbiotically with an airborne helicock, and they share the spoils. The mirrodillo attracts prey with its beautiful shining shell…
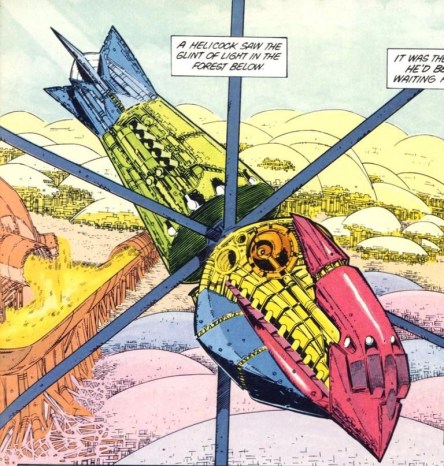
… prompting its helicock partner hovering above to fire a beam that reflects off the mirrodillo’s shell, causing indiscriminate damage to everything around it. The mirrodillo can then vacuum up its share while the helicock comes down to partake of the feast.

Mugger bugs are the descendants of car crushers, and have massive, crab-like bodies with powerful claws and huge mouths. The underbelly of a mugger bug is a powerful electromagnet that it uses to capture and disable prey before eating it and compressing it into a cube. Its back is covered with the remains of kills, effectively camouflaging it in plain sight. As you may have guessed, this is indeed something used in real life by assassin bugs, not to mention other insects as well. Technology imitates life. Or something.

Loco-constrictors, finally, are enormous snake-robots that evolved from trains, and still use the ruined rail system to get around. At least one of them, Nikku, was capable of generating paralyzing electrical shocks from the plates on her sides. She tries to eat Buboc, and gets chomped through by Amok for her trouble.
Metalzoic is © Pat Mills, Kevin O’Neill, DC Comics, 2000 AD, et al.
*Mekaka!